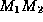 has the minimal travel time.
The two points are labeled A and B on Figure 1.1
The location of the point X on Figure 1.1 is determined by
the least travel time
has the minimal travel time.
The two points are labeled A and B on Figure 1.1
The location of the point X on Figure 1.1 is determined by
the least travel time 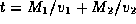 .
Hence
.
Hence
Fermat's principle states that of all possible paths joining two given
points on a wave path, the wave path has actual least travel time.
Figure 1.1 represents the situation where two media each
of constant velocity are separated by a plane interface.
The travel path 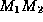 has the minimal travel time.
The two points are labeled A and B on Figure 1.1
The location of the point X on Figure 1.1 is determined by
the least travel time
has the minimal travel time.
The two points are labeled A and B on Figure 1.1
The location of the point X on Figure 1.1 is determined by
the least travel time 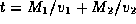 .
Hence
.
Hence
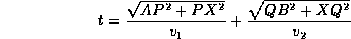
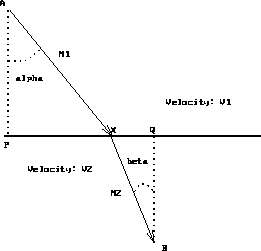
Figure 1.1: Fermat's Principle
Hence replacing PX= x-p and XQ= q-x, we obtain:
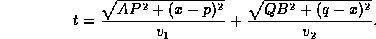
Differentiating t with respect to x, we obtain:
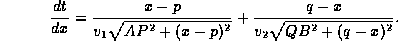
From calculus, we know that the minimum is achieved when
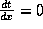 .
Hence the location of X is determined by solving the equation:
.
Hence the location of X is determined by solving the equation:
This is now a non linear relationship between the unknown value x and the data AP, p, q, QB. We devote the next section to solving this type of non-linear equations.
A final remark about Equation 1.1. Using basic trigonometry definitions, we observe that Equation 1.1 is nothing else than Snell's Law. The path of minimum travel time occurs at the point X at which Snell's law is satisfied.